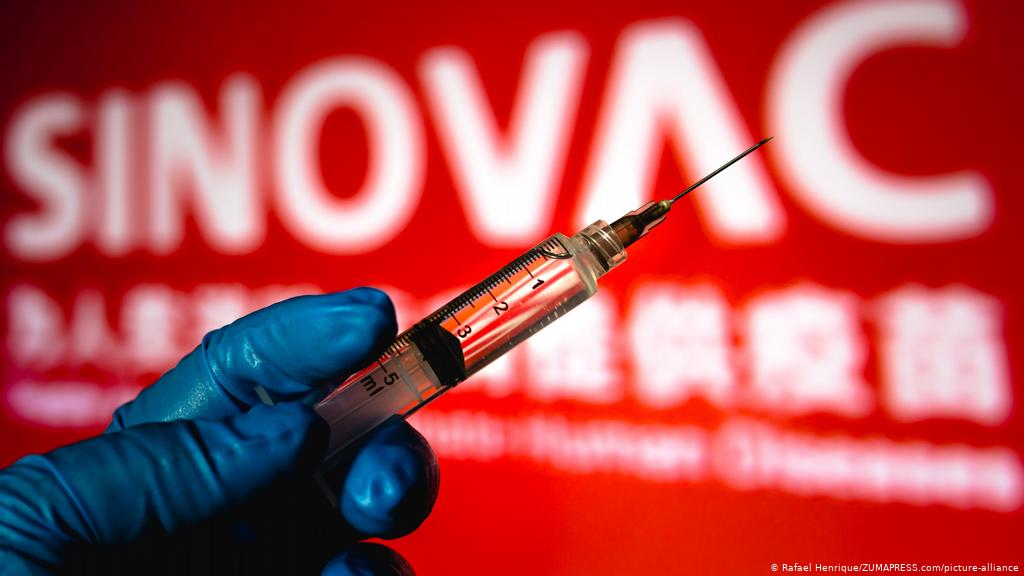
China’s leading Covid-19 vaccines secured their first emergency authorizations outside the country late last year, and were soon in use across the world. Adding together doses administered in China and overseas, they may be the most widely used Covid-19 vaccines globally.
The Chinese shots differ from the novel approach used by Moderna and Pfizer, which deploy messenger RNA (mRNA), genetic material that gives cells the instructions for mounting defenses against the coronavirus. Meanwhile Sinopharm and Sinovac developed inactivated Covid vaccines—using a neutralized version of the coronavirus to generate immunity.
Definition of Efficacy
Efficacy refers to the extent to which a vaccine reduces Covid-19 cases in a trial compared to the rate in a control group.
If a vaccine’s efficacy rate is 80% it doesn’t mean 20 out of every 100 people who get the jab will get a symptomatic case of Covid-19. Instead it means there will be 80% fewer such cases compared with the control group. So if , say, 1% of a control group of 1,000 unvaccinated people develops Covid-19 over a certain number of months, that means 10 people will get ill. With an efficacy rate of 80%, only 2 people should get sick.
But that’s not the only way to look at efficacy—there’s also efficacy against contracting a severe case, or against hospitalization for Covid-19. Shao Yiming, a researcher at the Chinese Centers for Disease Control, this month drew a distinction between protecting against infection, most likely referring to a positive but largely asymptomatic case, and against disease, ie an illness with one or more symptoms. The focus of vaccination in China is to “prevent people from getting ill [because of Covid-19], but not from getting infected,” said Shao.
The Sinopharm vaccines’ efficacy
China National Pharmaceutical Group, or Sinopharm, developed two vaccines, both via its subsidiary China National Biotec Group (CNBG).
Sinopharm said its BIBP vaccine, developed via subsidiary Beijing Institute for Biological Products, had an efficacy rate of 79% in a brief statement in December. But it only published interim results for its trials of both its shots last month, after the vaccine had secured World Health Organization emergency approval. That approval paves for more widespread acceptance, and for its distribution via Covax, a World Health Organization effort to share vaccines more equitably.
According to the World Health Organization factsheet for the BIBP vaccine, its trial was not “designed and powered” to show efficacy against severe disease in people with comorbidities, or older than 60, which is wording that is not included for the fact sheets for the Pfizer, Astra-Zeneca, Moderna, or SinoVac vaccines.
Sinopharm’s other vaccine, developed via a Wuhan unit and not listed for emergency use by the WHO, has an efficacy rate of around 73%.
The Sinovac vaccine’s efficacy data
Sinovac, the maker of the CoronaVac vaccine that’s being used in Indonesia, Brazil, and Chile, among other places, delayed the release of its trial data several times, before finally sharing the results from the trials on some 25,000 participants in February. It was approved by the WHO this month.
A Hong Kong review of its trial data showed an efficacy rate of around 62% while Brazil’s Butantan Institute, which tested the vaccine on frontline health workers, showed an an efficacy of 51% against mild disease and 100% against hospitalization. Smaller trials in Turkey and Chile showered higher rates of protection against mild disease.

Fresh doubts about China’s vaccines
New waves of Covid-19 cases in places with a high per capita level of Sinopharm or Sinovac vaccinations have raised concerns that the vaccines have lower real-world effectiveness than officials may have been hoping.
In the case of Chile, home to about 19 million people, that appears to have contributed to a consistently high new case count in recent months. An April study from the University of Chile put the effectiveness of a single dose of Covid-19 vaccine at 3% for protecting against symptomatic infection, based on an examination of seven million vaccinated people.
In tiny Seychelles, home to less than 100,000 people, some 60% of the population was fully vaccinated, but there was a surge in cases in May that forced fresh shutdowns. Of those with two doses, 57% got the Chinese vaccine while the rest got the Astra-Zeneca shot. More than a third of new cases were among the fully vaccinated, but the government hasn’t provided a breakdown for Sinopharm and Astra Zeneca among these cases.
Meanwhile Bahrain, which vaccinated about half its 1.6 million people with the Sinopharm vaccine but nevertheless battled a spike in cases starting in May, the government is offering a booster shot of the Pfizer vaccine to more vulnerable people, and the United Arab Emirates is doing the same. Officials in Bahrain have said, however, that the new cases were mostly among the unvaccinated.
In Uruguay, however, the government said this month that its vaccination campaign with the Sinovac vaccine had reduced deaths by 95% and intensive care admissions by 92%, in addition to reducing Covid-19 infections by about 60% in the country of 3.5 million. The country is also using the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine for people at higher risk, such as older people and health workers.
The biggest test of China’s vaccines may well come at home. After a slow start, the country has ramped up its domestic inoculation rate in recent weeks, with the Delta variant first seen in India contributing to a flare-up in the southern city of Guangzhou. China is now vaccinating 20 million people a day and has delivered 900 million doses so far, or enough to cover a third of its population.

 COVID-19 Around the World4 years ago
COVID-19 Around the World4 years ago
 Cuisine Explorer5 years ago
Cuisine Explorer5 years ago
 Tagalog5 years ago
Tagalog5 years ago
 Uncategorized5 years ago
Uncategorized5 years ago
 Cantonese - Traditional Chinese5 years ago
Cantonese - Traditional Chinese5 years ago
 Uncategorized5 years ago
Uncategorized5 years ago
 Uncategorized5 years ago
Uncategorized5 years ago