Features
The Dilemma of Elderly
Published
2 years agoon

Article/Blessing CALD Editorial;Photo/Internet
12 mins audio
Australia, ranking as the world’s sixth-largest country by land area, is an economically developed nation that is currently facing the challenge of an aging population. The proportion of Australians aged 65+ is continuously increasing, placing a growing burden on the younger workforce.
In the past 70 years, the proportion of people aged 65+ has doubled, and according to the latest annual population report by the Department of the Treasury, this trend is expected to accelerate. The aging population is primarily due to increased life expectancy and declining birth rates. The large baby boomer generation has contributed to Australia’s aging population. The direct consequence of this trend is the challenge of retirement and elderly care.
The Inescapable “Power of Attorney”
The Australian Human Rights Commission has published a booklet titled “Your Rights At Retirement: A guide to making decisions and navigating you through your later life.”, to explain the rights of older Australians and provide early preparation for potential issues. After all, various services, support, and decisions in retirement can be complex—such as income assistance, healthcare and aged care, senior cards, financial planning, retirement funds, housing, and rent subsidies, just to name a few. One common issue many older people may encounter is the establishment of a “Power of Attorney.”
As one grows older, there may come a time when they believe that designating someone else to make decisions on their behalf is in their best interests. This is commonly known as establishing a “Power of Attorney,” particularly when individuals are affected by conditions that impair decision-making or when they anticipate a future loss of decision-making capacity. In most cases, individuals grant a “Power of Attorney” to a trusted family member or chosen lawyer, government public trustee, or a combination of these individuals. It is crucial to take steps to establish a Power of Attorney well before losing the capacity to make independent decisions. If a person loses decision-making capacity before establishing a Power of Attorney, the government will appoint someone to make decisions on their behalf.
The Power of Attorney is a convenient but often overlooked legal arrangement. Especially with an Enduring Power of Attorney (POA), which allows an appointed person to act on behalf of the individual when they are unable to attend or have unfortunately lost cognitive/behavioral capacity. For instance, patients with severe dementia can appoint an enduring attorney while they are still of sound mind, enabling the appointed person to handle all matters related to medical care and property if the elderly person’s condition deteriorates and they lose mental clarity. This is particularly important for new immigrants, as many elderly Chinese individuals assume that their children will naturally handle their affairs, without realizing that the Australian system requires formal documentation of power of attorney to allow the appointed person to make decisions or handle medical and financial matters on behalf of the individual.

/Public guardians violating individual wishes and forcibly keeping elderly dementia patients in nursing homes
The Prisoners of the Country
System designs are ultimately ideal visions of humanity, but once they enter real life, the scenarios become diverse and complex. Not everyone has the foresight or awareness, nor the resources, to proactively plan their retirement affairs in a clear and explicit manner. So what happens when their health deteriorates? A recent report by ABC has prompted a reconsideration of the practical application of the “power of attorney” system. It’s hard to believe that such a story unfolds in Australia, a country known for its freedom, giving the impression of living in a nation without democratic liberties, unable to assert any individual rights.
The protagonist of the story is a man in his 70s from Western Australia who was diagnosed with suspected dementia in 2021. He has been forcibly confined in a nursing facility for over 16 months, incurring an annual cost of over AUD 75,000, and the crucial part is that this decision was not based on his personal wishes. The man’s brother, who served as his appointed representative, exercised his authority and placed him in the nursing facility against his will, despite his desire to remain living independently at home, as suggested by his family doctor.
Once admitted to the nursing facility, his brother no longer wanted to assume the responsibilities of being the appointed representative, and the facility handed him over to the government-appointed public trustee. The elderly man requested access to his own medical and financial information, but these are managed by the public trustee due to his diagnosis of dementia. He was denied access to his own healthcare and financial information, all in the name of protecting him. Currently, this elderly man is primarily under the control of two West Australian government agencies: the public trustee and the public advocate’s office. During a hearing held in February last year, there were no reports from geriatricians or psychiatrists regarding his dementia, nor any formal capacity assessments. The only medical evidence came from the nursing facility’s affiliated general practitioner, which led to the court’s final determination that the elderly man was “incapable of making reasonable judgments” and “unable to care for his own health and safety”. The Administrative Appeals Tribunal also confirmed that the court does not require expert evidence and that reports from general practitioners are often used as evidence. This raises doubts as to whether relying on evidence from the nursing facility poses a conflict of interest.
The plight of this elderly man is not an isolated case; it is happening to thousands of Australians. According to the law, if a person is deemed incapable of self-care and lacks family or friends to provide care, they will be assigned a public trustee and a public advocate. In Australia, every state and territory, except for the Australian Capital Territory, has similar laws, and it is estimated that 50,000 Australians with brain injuries, dementia, mental illness, or intellectual disabilities live under such orders. The public trustees manage over AUD 13 billion in assets belonging to these individuals, extracting millions of dollars in fees from their accounts annually, but due to privacy requirements, all of this is done behind a veil of secrecy.
Many people point out that while state governments establish public trustees, they do not provide funding, instead directly extracting fees from the assets of those under protection. This allows public trustees to view individuals with significant assets as cash cows, rather than acting impartially to protect them. It seems that in the case of this elderly individual, his substantial assets have become a means for the public trustee to violate his wishes and “imprison” him in a nursing facility.
Reform Cannot Be Delayed
Old age dementia, medically known as Alzheimer’s disease, requires guardianship and financial management for patients who have lost self-awareness. Although the medical field has devoted significant resources to research on treating dementia, there have not been significant breakthroughs so far. The period from September 1st to September 30th is Dementia Awareness Month, and it is important to recognize that old age dementia is not a normal part of aging. However, the Alzheimer’s Australia organization predicts that Australia will have approximately one million dementia patients by the middle of this century. The issue of caring for this population cannot be ignored.
Although individuals with dementia experience impacts on their memory, thinking, and daily functioning, it does not mean that their human rights should be violated. In other words, individuals with dementia should not be subjected to insults, discrimination, harm, or neglect. This raises the question of who determines the “best interests” of these elderly individuals and what role their own wishes play in the decision-making process. Over time, the condition of dementia patients deteriorates, but each case is unique. For patients in the early stages of the disease, whether it is in line with human rights to deprive them of the right to make decisions regarding their own affairs warrants discussion. Moreover, when it comes to a person’s well-being, a simple medical certificate may not be sufficient to legally determine their loss of cognitive capacity. Court assessments of whether someone is capable of making decisions regarding their health and finances or whether they require assistance need not only more evidence but also consideration of personal circumstances.
The current system of public trusteeship has been heavily criticized for its lack of accountability, high fees, and higher fees charged to those with assets. They have control over significant financial matters with minimal scrutiny, which undoubtedly constitutes a major intrusion into individuals’ lives, for which the government must assume its corresponding responsibility. Furthermore, as Australia is an immigrant society, older immigrants from diverse cultural backgrounds face additional challenges due to language, culture, and traditions. In recent years, with the release of the Royal Commission into Aged Care Quality and Safety final report, the call for significant reforms in Australia’s aged care industry has been growing. Fundamental reforms are urgently needed, whether in the aged care system itself or in its operations, funding support, and regulatory methods.
The Dilemma of Chinese Elderly
The Chinese community has limited and long-term understanding of the rights of the elderly, mainly due to the fact that most Chinese immigrants arrived in Australia in the late 1980s. Before the 1990s, Chinese immigrants were mostly in their thirties or forties, and there were not many elderly individuals at that time. The most well-known organizations that many people participate in, such as the The Chinese Senior Citizens Club of Manningham and the Box Hill Senior Citizens Club, celebrated their 35th anniversary last year, indicating that there were more 60+ aged Chinese seniors settling in Melbourne around 1987. Many times, they live with their children, and their lives are taken care of by the next generation.
However, the influx of Hong Kong immigrants in the 1990s and the trend of Chinese students immigrating after 2000, coupled with China’s one-child policy, led to the phenomenon of parents of international students becoming de facto retired immigrants. Suddenly, the number of Chinese seniors over the age of 60 increased significantly. Today, these seniors are in their 80s, and whether it is their care or issues related to illness, personal care, and their rights, it is evident that the Chinese community is ill-prepared.
Although the children of these seniors have received education in Australia, they may not be familiar with the Australian social system due to their relatively short time living in the country. When their parents encounter problems in managing their lives, they may not be able to assist them in finding solutions. If there are strained relationships with their children, if they do not live with their parents, or if they do not meet frequently, these seniors are easily left without assistance in their daily lives, and may not be able to find the best arrangements for themselves.
From Social Life to Care and Rights
Yes, indeed, for the past 35 years, the Chinese community has established numerous senior associations that have taken care of the social lives of elderly individuals. We have witnessed many seniors leading vibrant and colorful lives. Those who enjoy socializing have senior clubs, various educational classes, volunteer participation, performance groups, or church groups. However, as these seniors begin to experience physical decline, they require more care facilities and greater support in their daily lives. All of these aspects involve senior rights and personal life management.
Knowledge in this area is not widely introduced within the immigrant community, so most seniors are unaware and uninformed. Even mainstream society recognizes that senior rights are not adequately protected. It is time for us to pay more attention to the rights of our seniors and ensure that they can enjoy a safe and happy life in their later years after immigrating to Australia.
You may like
Features
What Is the Significance of Victorian Premier Jacinta Allan’s First Visit to China?
Published
4 days agoon
September 29, 2025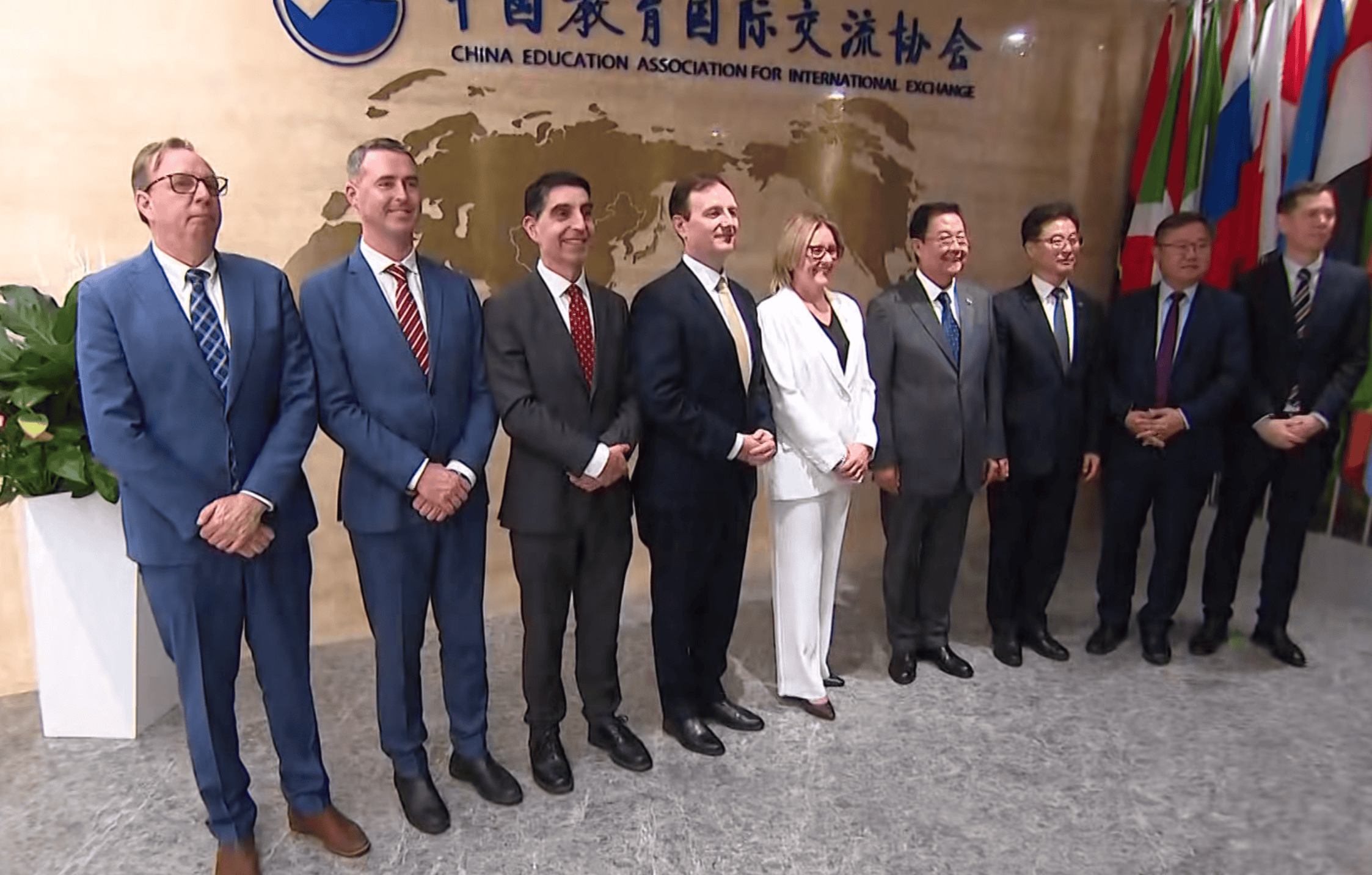
Victorian Premier Jacinta Allan embarked on her first visit to China since taking office, from September 14 to 19, lasting five days. Her itinerary included Beijing, Shanghai, as well as Victoria’s sister cities Nanjing, Chengdu, and Deyang. Accompanied by Labor MPs, she met with Chinese officials and business leaders. The focus was on boosting trade, promoting education exchanges, expanding the tourism market, and attracting more Chinese students and investment, with the aim of raising Victoria’s profile in China.
Is Victoria’s Relationship with China Over?
China has long been Victoria’s largest trading partner and the main source of international visitors. Allan’s office framed this trip as “the beginning of a new golden era” and emphasized that the purpose was to rebuild friendship with China.
Looking back, former premier Daniel Andrews had strongly promoted cooperation with China and even signed the “Belt and Road” agreement in 2018. However, the federal government later exercised its power under the Foreign Arrangements Scheme Act for the first time, canceling two agreements Victoria signed with China, citing inconsistency with Australia’s foreign policy or harm to foreign relations. This move provoked strong dissatisfaction from Beijing, with China’s Foreign Ministry harshly criticizing Australia for having “no sincerity in improving China–Australia relations.”
Subsequently, relations between China and Australia deteriorated further due to multiple controversies. Australia criticized Beijing’s actions regarding Hong Kong protests and human rights issues in Xinjiang, and supported the World Health Organization’s independent investigation into the COVID-19 outbreak. Meanwhile, Australian intelligence agencies exposed China’s attempts to influence local politics through political donations, sparking national security concerns. These events further strained bilateral ties.
Even so, Victoria tried to maintain exchanges with China, establishing sister-city relationships with several Chinese cities and consolidating ties through education and business cooperation, attempting to preserve collaboration within an otherwise tense climate.
But compared with Andrews’ “pro-China” image, Allan faces a more delicate situation. After stepping down two years ago, Andrews turned to private business, becoming a consultant with close links to Chinese enterprises. More recently, he even appeared at a military parade in Tiananmen Square and was photographed with President Xi Jinping and other Chinese leaders, sparking controversy. As the current premier, Allan has said, “”Victoria is an old friend of China and these connections are so valuable for our state,” but she must strike a far more cautious balance between cooperation with China and domestic political sentiment.
Judging by the arrangements of this visit, China’s reception of Allan was clearly not on par with that of Andrews in the past. She only met with Minister of Education Huai Jinpeng, and her first policy speech was held merely at a hotel. This treatment was far less prestigious than Andrews’ high-level invitation to witness the Tiananmen parade just a week earlier. Observers speculate that Beijing attaches limited importance to the current Victorian government, possibly because the “Belt and Road” agreements were overturned by the federal government, or due to the broader backdrop of strained China–Australia relations.
The Contradictions of Education Diplomacy
One major highlight of this trip was to deepen education cooperation. In its newly released Victoria’s China Strategy: For a New Golden Era, the Victorian government pointed out that in 2024 the international education industry contributed as much as AUD 15.9 billion to the state’s economy, remaining Victoria’s largest service export for more than two decades. Among this, Chinese students numbered 64,000, making China the largest source country. The document listed “continue to strengthen our reputation as a preferred destination for Chinese visitors, students, researchers, and investors” as a strategic priority, emphasizing the need to further consolidate Victoria’s image as a global destination for Chinese tourists, students, researchers, and investors.
When meeting Chinese Education Minister Huai Jinpeng in Beijing, Allan repeatedly stressed Victoria’s welcoming attitude toward Chinese students, hoping to expand bilateral exchanges through stronger educational cooperation and demonstrating the importance she attaches to “education diplomacy.”
However, this proactive approach sharply contrasts with federal policy. In August 2025, the Australian federal government announced a new student quota system, capping the total number of international students nationwide at 295,000 in 2026. Although this figure was 25,000 higher than the current year, industry insiders believe that due to persistent restrictions in the immigration system, actual numbers are unlikely to reach the cap. This runs counter to Victoria’s slogan of “saying yes to international students,” revealing a clear policy gap between the state and federal levels.
Under this contradictory framework, Victoria’s efforts to deepen cooperation with China through education remain constrained by federal policy, making it difficult for the state to achieve significant breakthroughs on its own. With the failed Belt and Road experience still fresh, it is understandable why Beijing did not devote much attention to the current premier. Against this backdrop, Allan could only meet with China’s education minister, raising doubts about how much real progress could be made.
Underwhelming Economic and Trade Outcomes
Just as politics offered little warmth, business results also proved lackluster. Many expected one of Allan’s key goals would be to seek Chinese funding for the Suburban Rail Loop (SRL) project, which faces a massive AUD 34 billion funding shortfall. This expectation was heightened by the fact that the rail line runs through electorates represented by several members of the delegation.
Yet, only a handful of business meetings were reported, with few major corporations participating. The visible results amounted to just two announcements: a solar energy cooperation project at the beginning of the trip, and at the end, the purchase of four tunnel boring machines (TBMs) from Chinese manufacturers for the SRL project.
The former was limited in scale and faced local criticism—during construction the project would create only about 60 temporary jobs, and after completion just six permanent positions, with minimal local employment benefits and potential environmental impacts.
The latter, although Allan made a point of visiting tunnel works in Deyang, Sichuan, and staged photo opportunities to emphasize Victoria’s cooperation with China, was essentially “spending money on imports.” While buying Chinese TBMs secured equipment for the SRL, it raised questions: why not develop or support such technology domestically, creating local jobs and industries, instead of sending huge sums abroad?
In other words, these arrangements mostly involved one-way capital outflow, without bringing in real foreign investment or capital inflows. The outcomes fell short of expectations for “attracting Chinese investment,” leaving only purchases and symbolic cooperation. With political recognition lacking and economic results unimpressive, what substantive benefits did this trip actually deliver for Victoria’s economy?
Economic Diplomacy or Electioneering?
For Allan, the trip was something of a dilemma. As premier, she could not avoid going to China during her term. But at the same time, she surely knew it would be hard to achieve real breakthroughs. The result was like a salesman being ignored despite enthusiasm, or a poor relative knocking on doors only to be turned away. Why, then, did Allan still lead a high-profile delegation to China?
Funded by taxpayers at an estimated cost of several hundred thousand dollars, the delegation did not include a single minister—only MPs from electorates with large Chinese or multicultural populations. They included Parliamentary Secretary and Box Hill MP Paul Hamer, and four Labor backbenchers: Meng Heang Tak (Clarinda), Mathew Hilakari (Point Cook), Matt Fregon (Ashwood), and John Mullahy (Glen Waverley).
According to the 2021 census, Victoria has around 500,000 residents of Chinese descent, a significant share of the state’s 7 million population. In these key electorates, Chinese voters number in the tens of thousands, enough to influence electoral outcomes. While these accompanying MPs may have little policy influence, they are politically important. This raises questions over whether Allan’s visit was more about connecting with the Chinese community ahead of the November 2026 state election, consolidating a large and crucial voter bloc. Rather than an economic diplomacy mission, it may have been a campaign-style political tour.
The trip delivered limited results, with symbolism outweighing substance. Allan brought back no new investment and no major corporate commitments, while her accompanying MPs became the focus. What can these powerless backbenchers actually bring to Victoria? Do they signal attention to multicultural communities and bolster diplomatic credentials? Or was this merely a “taxpayer-funded election show,” with taxpayer money spent on photo ops in China to build momentum for the next election? Anyone with a bit of political sense can see through it.
Multicultural Development
Just before the trip, the Victorian government released the Victoria’s Multicultural Review, regarded as the most significant policy reform in decades. Led by George Lekakis AO and an expert advisory group, it drew on 57 community meetings, consultations with over 640 residents, and input from more than 150 organizations and community groups. The goal was to strengthen social cohesion and rebuild trust between the government and multicultural communities. The report was released on September 11 by Allan and Minister for Multicultural Affairs Ingrid Stitt.
Core recommendations include establishing a new statutory agency, Multicultural Victoria, headed by a Multicultural Coordinator General, supported by two deputies (one from a rural area), and advised by a five-member commissioner panel. This structure would replace the largely ceremonial Victorian Multicultural Commission (VMC), which for years was limited to public relations without significant policy impact.
Following the review’s release, Allan quickly linked “multiculturalism” with the Chinese community. On September 12, in her hometown Bendigo, she announced nearly AUD 400,000 in funding to upgrade the Golden Dragon Museum into the “National Chinese Museum of Australia.” This symbolic move not only highlighted Bendigo’s historical ties to Chinese immigrants during the gold rush but also aimed to strengthen the cultural status of the Chinese community in Victoria.
Other funded projects included the Mingyue Buddhist Temple in Springvale South, the Avalokiteshvara Yuan Tong Monastery underground car park in Deer Park, the Museum of Chinese Australian History in Melbourne CBD, and infrastructure and lighting upgrades at the Chinese Association of Victoria Inc in Wantirna. These investments enhance cultural facilities and directly address community needs.
Is Multiculturalism a Political Tool or Genuine Goal?
This raises the question: are Allan’s initiatives genuinely aimed at fostering social cohesion, or are they part of political calculation? Victoria has long led the country in multicultural policy, but its political functions are also significant. During Andrews’ era, “multiculturalism” was used to package economic cooperation with China, drawing criticism of “national security risks” and “overdependence.” Allan now continues this approach but faces cool responses from Beijing and skepticism from the opposition and media at home.
Still, Allan’s strategy is not identical to Andrews’. Unlike the 2016 version of the “China Strategy,” her policy no longer emphasizes export figures or the economic benefits of the Belt and Road, but instead focuses more on cultural exchange and community engagement, encouraging Chinese-Australians to actively shape interactions with China. This shift highlights interpersonal and cultural connections rather than purely commercial transactions.
She has repeatedly wrapped her policies in “personal stories”: from Beijing to Nanjing to Shanghai, she promoted not just Victoria’s universities, tourism, and agricultural products, but also the importance of shared history, language, and culture. When meeting Education Minister Huai Jinpeng, she mentioned that her 13-year-old daughter is learning Chinese, to foster relatability.
Thus, Allan’s “multicultural strategy” carries two possible meanings: on one hand, it shows a sincere wish to improve social cohesion and strengthen ties with the Chinese community; on the other hand, it inevitably serves political calculation and election mobilization. As the 2026 state election approaches, Allan’s ability to convince both the Chinese community and the broader electorate that this is more than just political maneuvering but a genuine social vision will be a critical test of her leadership.
Still Unresolved: Practical Needs of Multicultural Communities
Even if Allan today offers small grants or gestures of goodwill toward the Chinese community, they pale in comparison to Andrews’ campaign promises in 2014 and 2018, when he pledged nearly AUD 20 million for the Chinese and Indian communities to purchase land for building aged care facilities. These two groups are now Victoria’s largest multicultural communities, and both place high cultural importance on caring for elders. Whether the elderly receive proper care in later life is a vital issue.
In 2018, the Australian government noted that as people live longer, the number of dementia patients is surging. For non-English-speaking elderly migrants—many of whom either never learned English or lose it due to dementia—the need for care in their native language and cultural context is especially acute. Yet mainstream services remain unwilling to provide such care. Therefore, the government has a responsibility to help minority communities build appropriate aged care facilities. Andrews recognized this situation and made it a campaign pledge.
But to this day, the Victorian government has only “purchased” the land and has not handed it over to community groups to build facilities—an 11-year failure that could be seen as the biggest “betrayal” of minority communities in Victorian history. By appealing to immigrant communities that value elder care, Andrews gained their votes to govern Victoria, but apparently never intended to deliver on his promises. It was a shameless act. Yet after Allan took over, she did not address the issue. Worse, last year she changed project rules, stripping Chinese and Indian community organizations of eligibility to apply to build aged care homes.
Clearly, the Allan government’s actions today sharply contradict its rhetoric about promoting multicultural development. This is likely to become a key concern for multicultural community voters in next year’s state election.
Features
From Everyday Pressure to Identity Anxiety: The Social Fault Lines Behind Anti-Immigration Marches
Published
3 weeks agoon
September 11, 2025On August 31, major Australian cities, including Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Canberra, Adelaide, Hobart, and Perth, simultaneously saw anti-immigration demonstrations under the banner “The March For Australia.”

The organizers rallied around the slogan “Oppose Mass Immigration”, claiming that immigrants were crowding housing and economic resources. In Melbourne, about 1,000 people participated, while Sydney saw a much larger turnout of 5,000 to 8,000 people. Marchers waved Australian flags, chanted “Australia”, and some shouted exclusionary slogans like “Go back” and “Stop the invasion.”
For newly arrived immigrants—or even residents who have already settled—such scenes were not only confusing but also alienating. Prime Minister Anthony Albanese pointed out in an interview that apart from Indigenous Australians, all Australians are either immigrants or descendants of immigrants. Australia’s history is rooted in Indigenous culture for tens of thousands of years, while large-scale European colonization has profoundly shaped modern Australian society. In other words, many of the demonstrators themselves may be descendants of immigrants—so why do they hold such strong anti-immigrant sentiments?

Anti-Immigration Marches Driven by Far-Right Ideology
The “March For Australia” was partly triggered by the “March for Humanity” pro-Palestinian demonstrations on August 3. On that day, Sydney saw 200,000–300,000 participants, with similar rallies in other cities. The marches were marked by Palestinian flags, some waving Hamas banners, and even portraits of Iran’s Supreme Leader Khamenei. These scenes stoked anxiety among some citizens about “foreign immigrants,” setting the stage for the anti-immigration march.
The organizers of “March For Australia” identified themselves as “patriots” or “ordinary Australians,” advocating against “mass immigration” and for the protection of national culture and identity. They heavily promoted the event on social media platforms like TikTok, X, and Facebook, emphasizing “only wave the Australian flag, no foreign flags” and using “Defend Australian values” as a slogan.
However, the march quickly drew criticism from the government and public opinion as “spreading hatred and dividing society.” One reason is the organizers’ links to far-right forces. According to the ABC, their website once cited the far-right white nationalist concept of “remigration”—calling for the large-scale deportation of non-European immigrants—and even featured pro-Nazi and Hitler memes. Although later removed, this suggested underlying far-right tendencies.
Controversy deepened with the public involvement of the neo-Nazi group National Socialist Network (NSN), which promotes white supremacy and anti-Semitism and openly idolizes Hitler. While organizers claimed they were only encouraging various groups to participate, NSN rhetoric and online platforms were easily co-opted by neo-Nazis and racists. On the day of the march, some NSN members shouted “Australia is for white people” and stormed Melbourne’s “Camp Sovereignty,” a symbolic Indigenous protest site, trampling flags and extinguishing sacred fires, accompanied by blatant racist slogans. This led mainstream media to label the march as far-right or even fascist.
A glaring contradiction arose: if the march’s core concern was social pressure from too many immigrants, why did some participants target Indigenous Australians and ethnic minorities? What could have been a debate on immigration policy turned into a stage for neo-Nazis exploiting social anxieties to promote white supremacy.
Moreover, the anti-immigration marches, under the guise of “patriotism,” unwittingly made some participants tools of neo-Nazi propaganda. For extremist groups, the immigration issue is just the easiest emotional lever; their true goal is to incite racial hatred and further divide society.
The Complexity of Participants’ Motives
The crowd was not monolithic. Besides hardline nationalists, there were residents genuinely concerned about the cost of living, including long-settled immigrants. In Sydney, when a speaker emphasized that “defending culture and lifestyle is not hatred,” the crowd cheered. But when a self-proclaimed “Australian white” leader called for a “new wave of nationalism,” some immediately voiced disapproval, shouting “This is hate speech!” and many left early. This demonstrates that even under the same “patriotism” slogan, legitimate grievances and extremist ideology coexist—highlighting the deep divisions within Australian society.
Notably, some first-generation immigrants participated in the anti-immigration march. They often distinguished between “low-skilled” or “illegal” migrants, whom they claimed could not integrate into Australian society, versus high-skilled or wealthy immigrants, whom they welcomed. This selective standard reveals hypocrisy: criticizing vulnerable groups from a position of relative advantage is still a form of xenophobia, and essentially, hate.
Perceptions vs. Reality of Immigration in Australia
Concerns over “mass immigration” were amplified during the “March For Australia”. Organizers emphasized worries over housing and economic resources but never clearly defined what “mass immigration” means. Australia has always been a nation of immigrants, and the perception of “too many immigrants” may not align with reality.
Data shows immigration has not continuously surged. According to the 2021 census, there were about 550,000 residents born in China, a 72% increase over a decade—but growth slowed to just 8% in the past five years. The Muslim population rose 70% between 2011 and 2021, but only from 2.2% to 3.2% of the total population. These groups remain a minority nationally, though their concentration in Sydney and Melbourne amplifies social perceptions.
The pandemic also played a role. Border closures temporarily reduced the number of international students and immigrants, but once borders reopened, net overseas migration (NOM) spiked to 340,000, mostly concentrated in Melbourne and Sydney. This compounded housing shortages and rising living costs, fueling social anxiety.
The Lowy Institute’s June 2025 national survey found that 53% of Australians believed immigration levels were “too high,” up 5% from the previous year; 38% saw it as “appropriate,” and only 7% said “too low.” Anxiety about “too many immigrants” is real—but the root issue may lie in chronic shortages of housing and infrastructure.
Population Growth and Pressure on Social Resources
According to the Australian Bureau of Statistics, net migration reached 446,000 in the year to June 2024, including 207,000 international students mostly on temporary visas. This population inflow strains public healthcare, education, transport, and social services: emergency wait times rise, classrooms are overcrowded, and public transport becomes congested. These pressures fuel public concern and skepticism of government planning.
However, the problem isn’t simply “too many immigrants,” but the gap between population growth and infrastructure planning. During the pandemic, net migration fell below zero, yet housing prices continued to soar, and healthcare and education systems remained under pressure. The post-pandemic rebound pushed net migration above 500,000 in 2023, largely from returning students and temporary workers. The challenge is whether government planning and investment can keep pace with population change.
Following the anti-immigration protests, the federal government announced on September 2 that the 2025–26 permanent migration program would maintain 185,000 spots, focusing on skilled migrants and family reunification. To “manage student numbers more sustainably,” the international student cap will rise to 295,000 in 2026.
From July 1, 2024, the government ended the 485 visa extension policy: bachelor’s and master’s graduates can stay a maximum of 2 years, research masters and PhDs up to 3 years. English proficiency requirements and visa fees increased. Previously, many 485 visa holders could extend automatically, even without permanent residency prospects, swelling the temporary resident population. Many worked low-skilled, low-wage jobs, further stressing social resources and labor markets.
The Labor government is gradually addressing these issues to better align immigration levels with resources. If measures succeed, gaps between population growth and social infrastructure could ease.
The Role and Contribution of Immigrants
Three common complaints about immigrants are: they depress wages, take jobs from locals, and drive up housing prices. While simple and catchy, these claims do not hold up to scrutiny.
Immigrants support key sectors in Australia. Healthcare has long faced labor shortages; international medical staff fill gaps. Technology, engineering, and IT sectors rely on overseas graduates for skills and innovation. Immigrant entrepreneurship creates jobs, benefiting locals and other migrants, fueling economic growth. Immigrants often sustain employment markets rather than “steal jobs.”
New migrants do face challenges, including language barriers, cultural adjustment, and job competition. Attributing employment pressure solely to immigrants ignores the difficulties they endure.
Regarding housing, data shows that during the pandemic, when immigration was at a century-low, house prices still soared—indicating that low interest rates, investment demand, land shortages, and rising construction costs were the main drivers. Population growth contributes to demand but is not the primary cause of high prices.
Anti-Immigration Sentiment and Australia’s Challenge
Immigration policy in Australia is both an economic necessity and a sensitive social issue. The anti-immigration marches exposed this tension: peace and violence, legitimate concerns and extremist ideology coexist.
As Federal Minister for Multicultural Affairs Anne Aly noted, far-right and neo-Nazi groups exploit real anxieties about housing and cost of living to spread hatred and xenophobia. Historically, blaming immigrants for housing and infrastructure issues has precedents—without clarification, such tendencies risk repeating.
The government also bears responsibility. Immigrants from diverse backgrounds have long been part of society, and associated issues are not new. Overreliance on specific source countries, inadequate regulation of international students staying on temporary visas, and lack of systemic planning for third-country immigrants are policy gaps. These delays turn structural problems into simplified “immigration issues,” which extremists exploit. Without improving resource allocation and planning, anti-immigration sentiment will deepen societal division.
In the long term, Australia’s true challenge is not simply “too many immigrants,” but balancing population pressure with multicultural integration. The historical White Australia Policy left a deep xenophobic imprint. Today, the government must strengthen housing and infrastructure planning and promote education and multicultural understanding to genuinely achieve the ideal of a diverse, inclusive Australian society.
Features
“Medisafe” Award Sparks Controversy; Debate Lasts Several Months
Published
3 weeks agoon
September 11, 2025Medisafe, developed by Pan Xichun, daughter of international liver cancer expert and honorary professor of surgery at the University of Hong Kong Pan Dongping, has participated in multiple major Hong Kong and international innovation competitions and won awards. However, it was challenged by Hailey Cheng, a second-year student in Computational Mathematics at City University of Hong Kong, who questioned the originality of the project, suggesting that Pan commissioned an AI company to develop Medisafe and entered it into competitions. This sparked months of controversy over “ethics and authorship.” Recently, Pan Dongping and his wife Peng Yongzhi issued a statement expressing willingness to relinquish Medisafe’s awards, though it remains unclear if this will temporarily end the months-long storm.

A Talented Young Student
Last year, Pan Xichun, a first-year student at the prestigious Saint Paul’s Co-educational College (SPCC) in Hong Kong, won numerous local and international awards for her AI project Medisafe. She received the Hong Kong ICT Award: Student Innovation Award, the Jury’s Special Commendation, and returned with honors from the Geneva International Invention Exhibition, earning media recognition as a “prodigy” and “future star of AI in healthcare.”

Medisafe is an AI-driven web application designed to assist hospitals and clinics in processing large volumes of prescriptions and connecting different medical departments, providing cross-hospital AI-assisted services for patients. The system cross-checks medications and patient databases to automatically verify allergies, long-term medications, and clinical conditions. It alerts medical staff if potential prescription or dosage issues are detected. In interviews after winning awards in April, Pan Xichun stated that the idea for Medisafe arose from news about medication errors. She emphasized that no similar system exists on the market that automatically compares prescriptions with patient medical records, claiming Medisafe as a first-of-its-kind concept.
Pan Xichun’s broader talents also highlight her capabilities: at 13, she founded a volunteer organization serving the community and earned recognition for musical talents. Previously, she created a system linking smart insoles to a mobile app to monitor hikers’ conditions and issue alerts, demonstrating creativity. Her outstanding performance from a young age is likely influenced by her family background, as her parents are established social elites.
Traditional Chinese educational philosophy stresses the role of parents and teachers as cultivators: “If a child is raised without proper teaching, it is the parent’s fault; if the teaching is not strict, it is the teacher’s laziness.” Pan Xichun’s early talents suggest her parents invested considerable effort in nurturing her abilities. From this perspective, it is hard to see why Pan Xichun’s parents should face criticism.
From Winning Awards to “Ethics Controversy”
The situation shifted quickly. On June 13, Hailey Cheng, a second-year student in computational mathematics at City University of Hong Kong and an undergraduate researcher in computational biology, posted on Threads questioning whether the project was solely Pan’s work. She also raised concerns about potential patient data leakage to third parties, citing privacy risks. This drew public attention: logging into Medisafe directed users to the AI Health Studio (AIHS) website, indicating clients included Pan Dongping and his brother Pan Dongsong’s Hong Kong Hepatopancreatobiliary and Colorectal Minimally Invasive Surgery Center. Subsequently, Medisafe became inaccessible.
As the controversy grew, AIHS co-founders issued a statement clarifying that in March of the previous year, they had been commissioned by Pan Dongping’s wife, Peng Yongzhi, to produce a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) for Medisafe. They emphasized the product was developed from scratch, with Pan Xichun providing only the initial idea, and that they were never informed it would be submitted to competitions.
Concerns arose over why an American AI company was hired. Peng Yongzhi explained that to prevent the concept from being copied or commercialized by others, she independently contacted the company in March of last year to explore developing a commercially viable product. In the same month, they were commissioned to develop the MVP for business feasibility verification. Competition organizers stress that entries must be original concepts created in Hong Kong, with participants holding intellectual property rights or legal ownership, and requested a full investigation by the Hong Kong Education City and the Standard Assurance Committee. Hong Kong Gifted Education Academy and Education City later confirmed that the platform was an original concept and that all awards would be retained. Nonetheless, controversies continued.
The Elite Mindset: Winning is Everything
In Hong Kong, a highly market-driven education system combined with entrenched social stratification makes competition extraordinarily fierce from the start. Children must not only learn early but also rely on substantial resources. Parental social status determines access to elite education, financial strength secures top-tier teachers, and extensive networks help package résumés. Education has become a precision investment: money, time, and strategy are invested, with expected returns in connections, résumés, platforms, and academic advancement. The Medisafe controversy offers a glimpse into this reality.
On a broader social scale, the Medisafe incident exposes a deep fissure in Hong Kong’s educational system: in a “competition-first” and “résumé-driven” environment, education becomes a theater for packaging success. The controversy is less about a “fallen prodigy” and more about public disillusionment with the “elite replication mechanism”—where awards reflect parents’ resources, connections, and wealth. Whether Pan Xichun is truly a genius or whether her family’s resources propelled her beyond societal expectations is now a topic of public debate.
Parents Step In
Recently, Pan Dongping and his wife announced they would relinquish all awards associated with Medisafe, citing their daughter’s mental and physical well-being as the priority. They acknowledged shortcomings in handling the situation, apologized for the disruption, and reaffirmed that Medisafe was Pan Xichun’s original concept. They also reserved the right to pursue legal action against false claims and malicious attacks online. Their statement reflects a protective parental stance, though it also reveals an elite mindset perceiving the world as being against their daughter.
In recent years, more than 4,000 Hong Kong students have participated in STEM competitions. Some schools even coach students “to win awards,” outsourcing development or fabricating research. This highlights the disparities in resources among families and raises questions of educational fairness. Education has become a contest of family background, capital, and packaging skills. The question arises: should children’s early growth aim to cultivate independent thinkers, empathetic and responsible individuals, or to produce elite performers following their parents’ scripts?
The Long Road Ahead
The most unfortunate aspect is the impact on Pan Xichun herself. Legally still a minor, she was thrust into a public controversy amplified by online discourse—a situation far beyond what a student should endure.
Online, critics labeled her actions as “academic fraud” or “winning awards through financial resources,” largely based on subjective assumptions without factual basis. STEM competitions are designed to encourage creativity and effort, not to judge minors by strict academic standards. Many online critics likely have no personal involvement in such competitions, but sensationalism elevated their importance beyond reason.
Pan Xichun’s parents hope relinquishing the awards will calm the storm, citing her extreme distress from online bullying. Rumors suggest she may take a year off school. Her recovery from this mental strain will vary and may leave long-term impacts. It is regrettable if public emotional venting hinders the development of an exceptionally talented young person.
However, the parents also criticized Hailey Cheng, asserting she was not a “well-intentioned whistleblower.” In reality, whistleblowers aim to raise public awareness, and their motives need not be “good-willed.” Critiquing social mechanisms often prompts backlash, but this does not invalidate whistleblowing. Cheng consistently updated the situation online since June, reportedly facing online and real-world harassment, including anonymous threats, which is also unacceptable.
After Pan’s parents announced relinquishing the awards, Cheng noted that their decision was not due to competition rules or originality disputes but primarily to protect their daughter’s health, highlighting how formal mechanisms often fail while online discourse pressures change. This reflection raises questions: can evidence, rules, and facts truly drive investigations, or only public pressure and online debate? Elite families may perceive rules and evidence as tools to climb social ladders—until public scrutiny, particularly online, challenges their arrogance.
When competitions intended to promote innovation and discover young talent become contests of academic resources and connections, one must ask: how much space remains for ordinary children to advance? Family legacy requires generational continuity, but when social mechanisms reinforce inequality and disregard basic fairness, whistleblowing deserves attention.
Listen Now

QantasLink Considers Closing Staff Bases in Canberra, Hobart, and Mildura
ACMA Issues Warning to “The Kyle and Jackie O Show”
British Primatologist Jane Goodall Passes Away
NSW Police Urged to Stop Strip-Searching People
Israeli Navy Intercepts “Global Sumud” Aid Flotilla; Greta Thunberg Detained
Fraudulent ivermectin studies open up new battleground

Cantonese Mango Sago

FILIPINO: Kung nakakaranas ka ng mga sumusunod na sintomas, mangyaring subukan.

保护您自己和家人 – 咳嗽和打喷嚏时请捂住

如果您出現以下症狀,請接受檢測。

U.S. Investment Report Criticizes National Security Law, Hong Kong Government Responds Strongly

China Becomes Top Destination for Australian Tourists, But Chinese Visitor Return Slows

What Is the Significance of Victorian Premier Jacinta Allan’s First Visit to China?

Albanese Visit to UK Focuses on Domestic Reform, Not Republican Debate

Optus Faces Another “000” Outage, Singtel Bonus Sparks Controversy
Trending
-
 COVID-19 Around the World4 years ago
COVID-19 Around the World4 years agoFraudulent ivermectin studies open up new battleground
-

 Cuisine Explorer5 years ago
Cuisine Explorer5 years agoCantonese Mango Sago
-

 Tagalog5 years ago
Tagalog5 years agoFILIPINO: Kung nakakaranas ka ng mga sumusunod na sintomas, mangyaring subukan.
-

 Cantonese - Traditional Chinese5 years ago
Cantonese - Traditional Chinese5 years ago保护您自己和家人 – 咳嗽和打喷嚏时请捂住
-

 Uncategorized5 years ago
Uncategorized5 years ago如果您出現以下症狀,請接受檢測。
-

 Uncategorized5 years ago
Uncategorized5 years agoCOVID-19 檢驗快速 安全又簡單
-
Uncategorized5 years ago
在最近的 COVID-19 應對行動中, 維多利亞州並非孤單
-
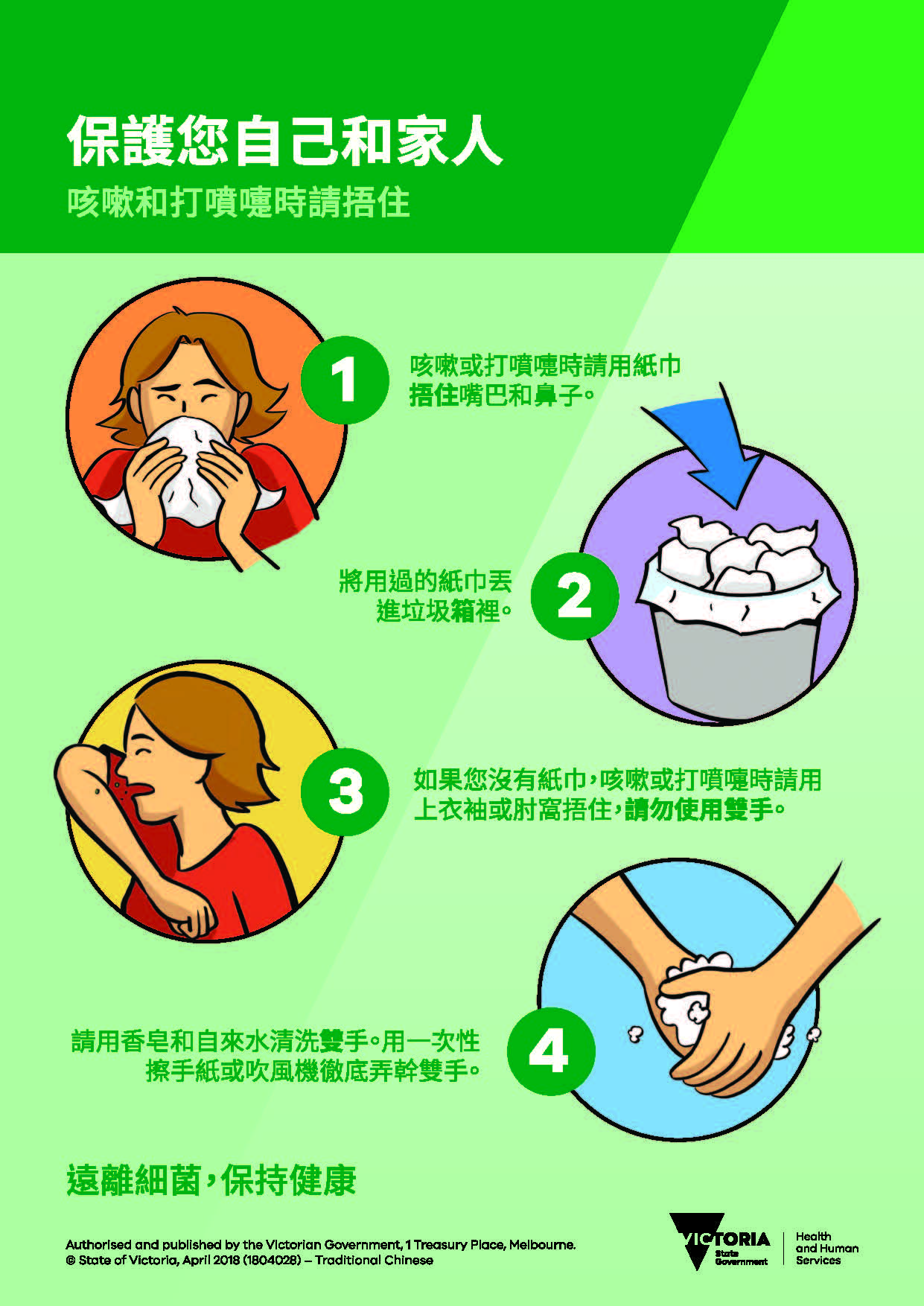
 Cantonese - Traditional Chinese5 years ago
Cantonese - Traditional Chinese5 years ago保護您自己和家人 – 咳嗽和打噴嚏時請捂住


